Introduction to the key parameters and indicators of the digital multimeter. The digital multimeter must be familiar to all electronic and electrical engineers. Digital Multimeter (DMM) is an electronic instrument used in electrical measurement. It can have many special functions, but its main function is to measure the voltage, current, resistance, on-off and other electrical parameters. As a modern multi-purpose electronic measuring instrument, it is mainly used for electrical maintenance, equipment maintenance, R&D testing and other applications.
What key indicators should we first consider when selecting a digital multimeter?
1。 Test principle
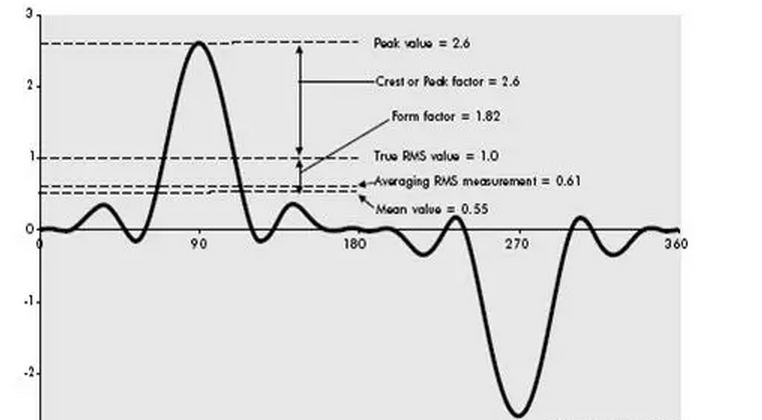
There are two testing principles of digital multimeter: average response and true RMS, which correspond to different types of electrical signal testing.
For DC signal or standard sine wave, instruments with true RMS or average response can measure accurately; But for signals with distorted waveforms, or typical non sinusoidal waves such as square wave, triangular wave, sawtooth wave, only true RMS instrument can accurately measure.
P. S: For more introduction to the principle, please refer to the second part of the history lecture - Why is the true RMS test so important
2。 bandwidth
Bandwidth is the AC frequency range that the digital multimeter can respond to within the accuracy range. It is not the function of measuring frequency, but the ability to reflect the AC frequency response. If the measured signal frequency exceeds the AC bandwidth of the multimeter, the multimeter will not be able to correctly measure the AC value within the frequency response range.
For example, the measuring range of Fluke115C multimeter test frequency is 50KHZ, but the bandwidth is 500HZ. This means that when F115C is used to test the frequency parameters of the signal, the maximum value can reach 50KHZ. However, when the frequency of the measured signal exceeds 500HZ, if F115C is used to test the voltage/current parameters of the signal, there will be a large error in the test results, so a meter with appropriate bandwidth should be selected to test the corresponding signal
3。 range
Range refers to the maximum value that the instrument can test in the current gear. The appropriate measuring range shall be selected according to the range of the measured signal value. Fluke multimeters are all manual/automatic measuring ranges, which are convenient for users to switch freely.
When selecting a digital multimeter, it is necessary to select a meter with a suitable range according to the actual test requirements.
4。 Display digits and resolution
Display digits: the range of words that the multimeter can display.
Generally, the digits that can display all digits from 0 to 9 become integer digits, and the others are collectively referred to as half digits.
For example, Fluke15B+has 3999 display digits, only three positions can display all 0-9, and the highest position can only display 0-3, so it is called a three and a half digit table. The Fluke 87-VC has a display digit of 19999. There are four positions where all 0-9 can be displayed. The highest position can only display 0-1, so it is called a four and a half digit table.
Resolution: describes the minimum change of identifiable physical quantity.
The resolution of some specific readings is determined by the height of the digits displayed on the half of the multimeter and the size of the digits displayed on the multimeter. The larger the number of display digits, the higher the resolution of the instrument when testing.
For example, the number of display digits of Fluke15B+is 3999, the number of display digits of Fluke115C is 5999, and the number of display digits of Fluke287C is 49999.
If the actual value of the current measured voltage is 402.6V, Fluke15B+will display 402V, which can distinguish the change of 1V level signal. Fluke115C will display 402.6V, which can distinguish the change of 0.1V signal. The Fluke287C will display 402.60V, which can distinguish the change of 0.01V level signal.
5。 Other special functions
Other functions, such as low-pass filter, double impedance input, temperature and other auxiliary functions, shall be reasonably selected according to the actual test requirements and the type of signal to be tested.
Sharp tools make good work!
Therefore, in the model selection stage, appropriate tools should be selected according to the type and requirements of the actual measured signal. The most appropriate digital multimeter can help you achieve your mission.



 Your location:
Your location: